Underground storage tank (UST) leaks from a former gas station contaminated shallow ground water under a parking lot for a commercial building. The UST contamination was found during trenching for utilities. As the presence of contamination prevented further property development, fast remediation was important to the stakeholders.
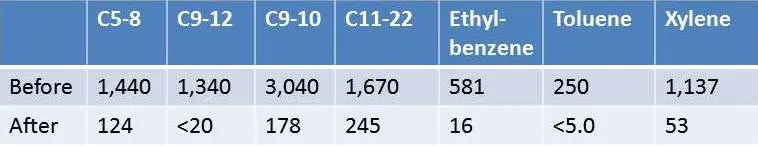
The size of ground water plume that resulted from leaching soil contaminants was estimated to be 5,000 square feet. The contamination was mainly diesel-range petroleum constituents, with the highest concentrations in the aliphatic range, but there were also scattered detections of xylene, toluene, and ethylbenzene.
Petrox bioremediation was implemented in the ground water. Three units of Petrox (165 gallons) were injected into the contaminated ground water through vertical injection wells located up gradient of the monitoring wells.
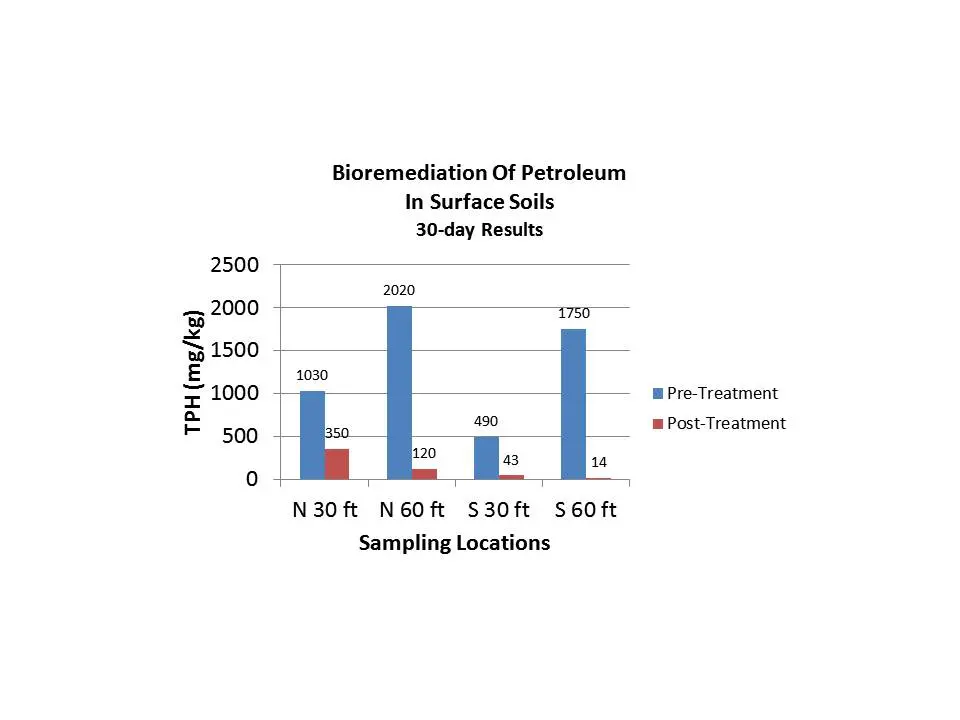
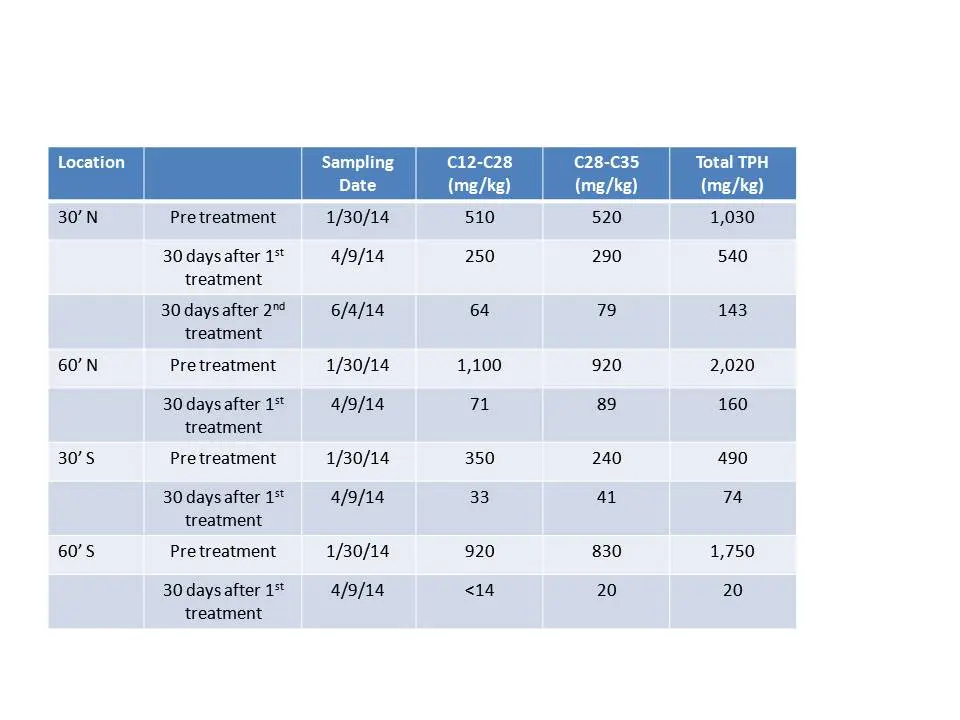
After a single inoculation of Petrox, the contaminant concentrations were reduced across the property. The following table shows the overall reduction in both the volatile and semi-volatile range hydrocarbons.